Authors : Tamar Zelovich, Leslie Vogt, Dario R Dekel, Michael Hickner, Chulsung Bae, Stephen J Paddison,
Mark E Tuckerman
Regardless of the initial hydration level, a typical Anion Exchange Membranes (AEMs) fuel cell device would operate ultimately under extremely low hydration values. It is therefore vital to fully explore the hydroxide diffusion in AEMs under such conditions. In this work, we present fully atomistic ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) simulations to obtain a molecular-level understanding of the hydroxide solvation complexes and diffusion mechanism in low hydration AEMs. By changing the polymer electrolyte cation spacing and the hydration values we create three different
Authors: Dario R Dekel, Igal G Rasin, Simon Brandon
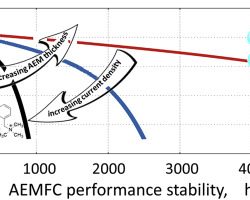
Anion-exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs) are attracting increasing attention worldwide mainly due to this technology's potential to considerably reduce fuel cell device costs. However, their development and implementation is significantly handicapped by the membrane and ionomer's decomposition during cell operation. In this study we propose and apply a unique one-dimensional model capable of predicting, for the first time, the performance stability of AEMFCs. The model accounts for the ionomeric material degradation and its relationship with local hydration, which depends on cell material properties, design parameters and operating conditions. Using this model, we
Authors: Haoran Yu, Elena S Davydova, Uri Ash, Hamish A Miller, Leonard Bonville, Dario R Dekel, Radenka Maric
The development of Pt-free catalyst for anion exchange membrane fuel cells is limited by the sluggish hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) at the anode. Previously, the use of CeO2 as a catalyst promoter facilitated drastic ennoblement of Pd for the HOR kinetics in base media. However, further optimization and understanding of the Pd–CeO2interaction, surface properties, and their influence on HOR are still needed. In this work, three types of Pd–CeO2/C catalysts are synthesized by a flame-based process, where the Pd–CeO2 interface and the HOR activity are
Electrospun Ionomeric Fibers with Anion Conducting Properties
Authors : Meirav Mann‐Lahav, Manar Halabi, Gennady E Shter, Vadim Beilin, Moran Balaish, Yair Ein‐Eli, Dario R Dekel, Gideon S Grader
Anion conductive nanofiber mats from FAA‐3 ionomers are obtained by electrospinning. Depending on the solvent used in the precursor solution, nanofibers with either nonhollow cylindrical or flat ribbon‐like cross‐sections are prepared. The anion conductivity and water uptake of the ionomeric nanofiber mats are measured as a function of the relative humidity in the 10–90% range and compared to that of a solid membrane cast from the same ionomer. In addition, the anion conductivity of
Authors : Israel Zadok, Dario R Dekel, Simcha Srebnik
Hydroxide ion transport and structure in aqueous media is fundamental to many chemical and biological processes. Research on hydroxide behavior has primarily focused on a single fully solvated hydroxide, either as an isolated cluster or in the bulk. This work presents the first computational study to consider a medium of low hydration levels where the hydroxide ion is microsolvated. Under such conditions, hydroxide ions are shown to be predominantly present as unique water-bridged double-hydroxide charged clusters, distinct from previously reported structures under hydrated conditions. Although layered double hydroxides were reported in the
Author: Dario R Dekel
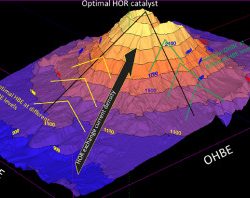
Anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs) can potentially revolutionize the energy generation market; however, to be seriously considered as a real alternative to the mainstream fuel cell technology, complete removal of previous metal electrocatalysts needs to be achieved. While in cathode electrodes platinum can be easily substituted, the electrochemical hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) in the AEMFC anodes currently involves prohibitive overpotential losses, making the removal of platinum extremely challenging. Understanding the HOR in AEMFCs will facilitate the path to overcome the challenge and finally develop and demonstrate platinum-free high-performance AEMFC devices.
Authors : Elena S Davydova, Jérémie Zaffran, Kapil Dhaka, Maytal Toroker, Dario Dekel
Carbon supported nanoparticles of monometallic Ni catalyst and binary Ni-Transition Metal (Ni-TM/C) electrocatalytic composites were synthesized via the chemical reduction method, where TM stands for the doping elements Fe, Co, and Cu. The chemical composition, structure and morphology of the Ni-TM/C materials were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The electrochemical properties towards hydrogen oxidation reaction in alkaline medium were studied using the rotating disc electrode and cycling voltammetry methods. A
Authors: S Maurya, J H Dumont, C N Villarrubia, I Matanovic, Dongguo Li, Y S Kim, S Noh, J Han, C Bae, H A Miller, C H Fujimoto, Dario R Dekel
Material interactions at the polymer electrolytes–catalyst interface play a significant role in the catalytic efficiency of alkaline anion-exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs). In this work, the surface adsorption behaviors of the cation–hydroxide–water and phenyl groups of polymer electrolytes on Pd- and Pt-based catalysts are investigated using two Pd-based hydrogen oxidation catalysts—Pd/C and Pd/C-CeO2—and two Pt-based catalysts—Pt/C and Pt-Ru/C. The rotating disk electrode study and complementary density functional theory calculations indicate
Authors : Charles E Diesendruck, Dario R Dekel
Anion exchange membrane fuel cells can potentially revolutionize energy storage and delivery; however, their commercial development is hampered by the chemical decomposition of the anion exchange membranes during operation. The hydroxide anions, while transported from the cathode to the anode, attack the positively charged functional groups in the polymer membrane, neutralizing it and suppressing its anion-conducting capability. In recent years, several new quaternary ammonium salts have been proposed to address this challenge, but while they perform well in ex-situ chemical studies, their performance is very limited in real fuel cell studies. While cation
Authors : Sinai Aharonovich, Nansi Gjineci, Dario R Dekel, Charles E Diesendruck
Tetraaryl ammonium salts are a synthetic challenge, since there is no general method for the arylation of triaryl amines. Contrary to other quaternary ammonium salts, tetraaryl ammonium salts should be very chemically stable. The ipso carbons are not very electrophilic, since the positive charge is distributed throughout the pi systems and they have no acidic β hydrogens. Here we demonstrate a simple approach to N,N-diphenyl carbazolium salts using only three synthetic steps, allowing for an easy production of these salts in large amounts and in a relatively short time.