Authors: Noga Ziv, Dario R Dekel
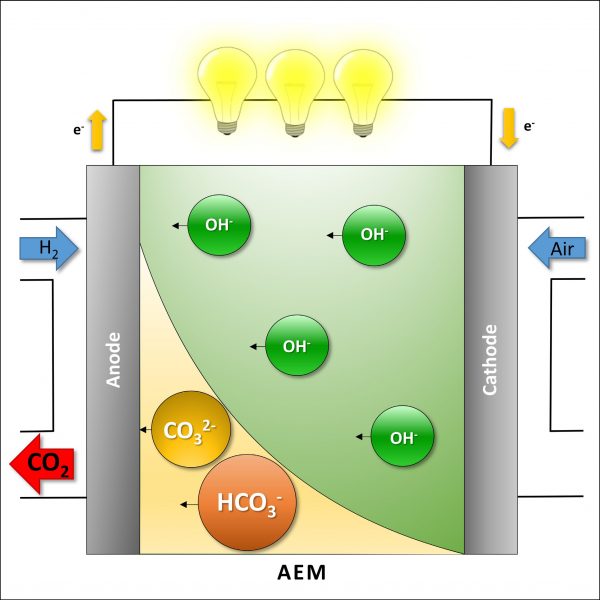
Hydroxide ions in anion exchange membranes (AEMs) are quickly exchanged for larger and less mobile anions (CO₃2− and HCO₃−) when the membrane is exposed to ambient air. Therefore, reported conductivity values of AEMs in hydroxide form are difficult to reproduce, and existing conductivity measurement techniques are not always reliable. Up to now, comparison of reported data for the hydroxide conductivity of different membranes has not been possible because tests have been performed not just with different anions, but also under different conditions and using different methods. In this work we present a practical and reproducible ex situ method for measuring the true value of the hydroxide conductivity of AEMs.